SURGICAL INSTRUMENTS
SURGICAL INSTRUMENTS – Precision Tools for Optimal Surgical Performance
Surgical instruments are specialized tools crafted to assist surgeons in performing precise and complex procedures. These instruments are fundamental to successful surgical outcomes, supporting a wide range of tasks from cutting and dissecting to suturing and tissue handling.
- Types of Surgical Instruments
Surgical instruments are categorized based on their function, with each category designed to perform specific tasks:
- Cutting and Dissecting Instruments: Tools such as scalpels, scissors, and dissectors used for making incisions and separating tissues.
- Grasping and Holding Instruments: Includes forceps and clamps for holding, pulling, or positioning tissues during procedures.
- Retracting Instruments: Retractors are designed to hold back tissues or organs, providing better visibility and access to the surgical area.
- Clamping and Occluding Instruments: Hemostats and clamps are used to control bleeding by compressing blood vessels or tissues.
- Suturing and Stapling Instruments: Needles, needle holders, and staplers allow for closing incisions or securing tissues during surgery.
- Importance of Surgical Instruments in Healthcare
Surgical instruments are integral to ensuring successful surgical outcomes. Precision instruments allow for controlled and safe procedures, reducing risks and improving patient recovery.
- Precision and Control: High-quality surgical tools provide surgeons with the control necessary for delicate operations.
- Minimizing Tissue Damage: Specialized tools designed for specific tasks help prevent unnecessary tissue damage.
- Reducing Surgical Time: Efficient instruments can help streamline procedures, reducing operating time and improving patient safety.
- Enhanced Surgical Outcomes: Proper instruments enable surgeons to perform procedures accurately, which is critical to patient recovery and overall success.
- Commonly Used Surgical Instruments
- Scalpel: Sharp blade used for making precise incisions.
- Forceps: Tweezer-like tools for holding or manipulating tissues.
- Hemostat: Clamping tool for controlling bleeding.
- Scissors: Surgical scissors come in various designs for cutting tissues or sutures.
- Needle Holder: Holds the needle during suturing for controlled and precise stitching.
- Retractors: Tools that hold back tissues to expose the surgical site.
- Care and Maintenance of Surgical Instruments
- Sterilization: Ensures instruments are free of contaminants, reducing infection risks.
- Regular Inspection: Identifies signs of wear or damage, ensuring safe and efficient use.
- Proper Storage: Prevents damage and prolongs the life of instruments.
Conclusion
Surgical instruments are essential tools that empower surgeons to perform complex procedures with precision and care. The quality and functionality of these instruments are directly linked to patient outcomes, making them a critical component in any surgical setting.
Showing all 13 results
-
Hernia Mesh
Add to Cart -

Medical Nylon Thread
Add to Cart -
Nasal Speculum
Add to Cart -
Pelvic Traction Kit
Add to Cart -

Uterine Dilator
Add to Cart -
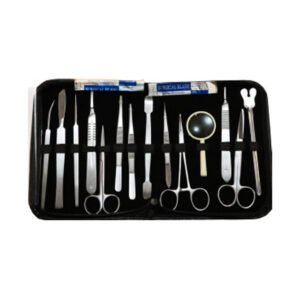
Dissecting Set
Add to Cart -

Vaginal Speculum
Add to Cart -

GalliPot With Lid
Add to Cart -

Instrument Tray
Add to Cart -

Kidney Tray
Add to Cart -

Surgical Scissors
Add to Cart -

Dressing Drum
Add to Cart -

Forceps and Holders
Add to Cart
